Capsaicin
IUPAC Name: 8-Methyl-N-Vinillyl-trans-6-nonenamide
CAS #: 404-86-4
CAS #: 404-86-4
Properties
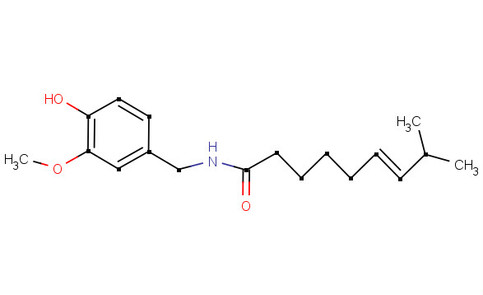
Molecular Formula: C18H27NO3
Molecular Weight: 305.41 g/mol
Boiling Point: 210–220 °C
Melting Point: 62–65 °C
Pure Capsacin: White or dull tan color
Structural Formula: ------------------>
Stereoisomer: 0
Chiral Centers: 0
Functional Groups/IR Spectrum:
Molecular Weight: 305.41 g/mol
Boiling Point: 210–220 °C
Melting Point: 62–65 °C
Pure Capsacin: White or dull tan color
Structural Formula: ------------------>
Stereoisomer: 0
Chiral Centers: 0
Functional Groups/IR Spectrum:
- Alcohol group: 3200-3600
- Alkene: 1620-1680
- Benzene Ring: 1450-1650
- Ether: 1000-1280
- Ketone: 1680-1750
- Secondary Amine: 3200-3500
Medicinal Uses
Capsaicin
is currently used in topical ointments, as well as a high-dose epidermal patch. It relieves the pain of peripheral neuropathy, such as post-herpetic neuralgia caused by shingles. It also works as an arthritis reliever. The American Association for Cancer Research reports studies suggesting
capsaicin is able to kill prostate cancer cells by causing them to undergo apoptosis. The studies were performed on tumors formed by human prostate
cancer cell cultures grown in mouse models, and
showed tumors treated with capsaicin were about one-fifth the size of the
untreated tumors. There have been several clinical studies conducted in Japan
and China that showed natural capsaicin directly inhibits the growth of
leukemic cells.
Hazards
Capsaicin is the active ingredient used in pepper spray. Although it is very strong eye irritant, it is not lethal unless large amounts of pure capsaicin are consumed.
